Overview
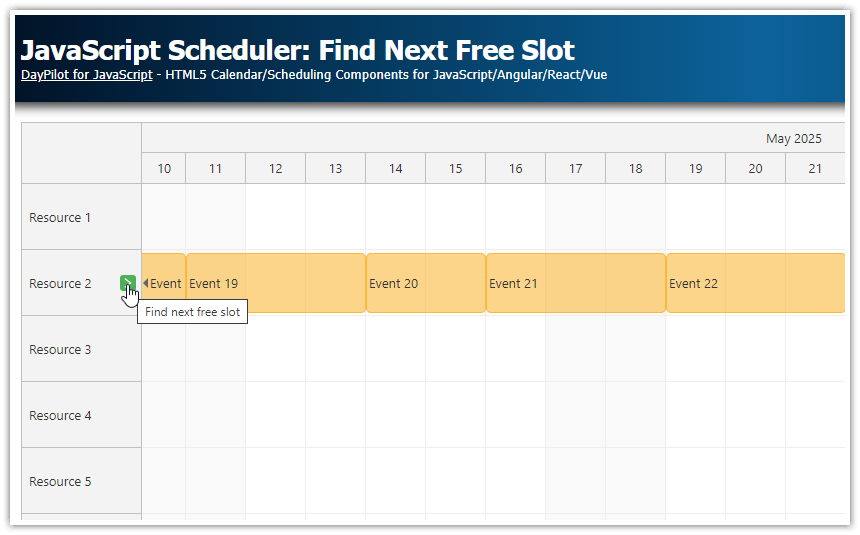
How to create custom buttons that navigate to the next event outside the viewport in a JavaScript Scheduler with sparse data.
Finding the Next Event Outside the Viewport

First, we need to get a list of events and sort them by start date:
const events = scheduler.events.all().sort((a, b) => a.start().getTime() - b.start().getTime());The events.all() method returns an array of DayPilot.Event objects in the original load order. To ensure chronological order, we call .sort() on the array, comparing each event’s start date/time.
To make this reusable, define an eventsSortedByStart() helper:
eventsSortedByStart() {
return scheduler.events.all().sort((a, b) => a.start().getTime() - b.start().getTime());
},Now we can focus on the current viewport boundaries.
To get viewport details, use the getViewport() method:
const viewport = scheduler.getViewport();This returns an object with start and end dates (among other properties). For the next-event logic, we only need the viewport end:
const { end: viewportEnd } = scheduler.getViewport();The following line finds the first event that starts after the viewport ends:
const nextEvent = this.eventsSortedByStart().find(e => e.start() >= viewportEnd); If such an event exists, scroll to it (with animation). Otherwise, show a message:
if (nextEvent) {
scheduler.scrollTo(nextEvent.start());
} else {
DayPilot.Modal.alert("No next event found");
}Finally, bind this logic to a “Next” button click handler:
this.elements.scrollToNext.addEventListener("click", () => {
const { end: viewportEnd } = scheduler.getViewport();
const nextEvent = this.eventsSortedByStart()
.find(e => e.start() >= viewportEnd); // completely after the viewport
if (nextEvent) {
scheduler.scrollTo(nextEvent.start());
} else {
DayPilot.Modal.alert("No next event found");
}
});Finding the Previous Event Outside the Viewport

The “Previous” button follows the same pattern, but we reverse the sorted list and look for events ending before the viewport starts:
const prevEvent = this.eventsSortedByStart()
.reverse()
.find(e => e.end() <= viewportStart);Bind it to the click handler:
this.elements.scrollToPrev.addEventListener("click", () => {
const { start: viewportStart } = scheduler.getViewport();
const prevEvent = this.eventsSortedByStart()
.reverse()
.find(e => e.end() <= viewportStart);
if (prevEvent) {
scheduler.scrollTo(prevEvent.start());
} else {
DayPilot.Modal.alert("No previous event found");
}
});Full Source Code
Below is the JavaScript source code of the example.
import {DayPilot} from "@daypilot/daypilot-lite-javascript";
const scheduler = new DayPilot.Scheduler("scheduler", {
timeHeaders: [{groupBy: "Month"},{groupBy: "Day", format: "d"}],
scale: "Day",
days: 365,
startDate: "2026-01-01",
timeRangeSelectedHandling: "Enabled",
onTimeRangeSelected: async (args) => {
const scheduler = args.control;
const modal = await DayPilot.Modal.prompt("Create a new event:", "Event 1");
scheduler.clearSelection();
if (modal.canceled) { return; }
scheduler.events.add({
start: args.start,
end: args.end,
id: DayPilot.guid(),
resource: args.resource,
text: modal.result
});
},
eventBorderRadius: 6,
durationBarVisible: false,
onBeforeEventRender: args => {
args.data.backColor = "#f1c232cc";
args.data.borderColor = "darker";
},
});
scheduler.init();
const app = {
elements: {
scrollToPrev: document.getElementById("scrollToPrev"),
scrollToNext: document.getElementById("scrollToNext")
},
loadData() {
const resources = [
{name: "Resource 1", id: "R1"},
{name: "Resource 2", id: "R2"},
{name: "Resource 3", id: "R3"},
{name: "Resource 4", id: "R4"},
{name: "Resource 5", id: "R5"},
{name: "Resource 6", id: "R6"},
{name: "Resource 7", id: "R7"},
{name: "Resource 8", id: "R8"},
{name: "Resource 9", id: "R9"},
];
// sparse to test scrolling
const events = [
{
start: "2026-01-02T00:00:00",
end: "2026-01-04T00:00:00",
id: "1",
resource: "R2",
text: "Event 1"
},
{
start: "2026-05-02T00:00:00",
end: "2026-05-05T00:00:00",
id: "2",
resource: "R2",
text: "Event 2"
},
{
start: "2026-09-01T00:00:00",
end: "2026-09-03T00:00:00",
id: "3",
resource: "R4",
text: "Event 3"
}
];
scheduler.update({resources, events});
},
eventsSortedByStart() {
return scheduler.events
.all()
.sort((a, b) => a.start().getTime() - b.start().getTime());
},
init() {
// previous
this.elements.scrollToPrev.addEventListener("click", () => {
const { start: viewportStart } = scheduler.getViewport();
const prevEvent = this.eventsSortedByStart()
.reverse()
.find(e => e.end() <= viewportStart);
if (prevEvent) {
scheduler.scrollTo(prevEvent.start());
} else {
DayPilot.Modal.alert("No previous event found");
}
});
// next
this.elements.scrollToNext.addEventListener("click", () => {
const { end: viewportEnd } = scheduler.getViewport();
const nextEvent = this.eventsSortedByStart()
.find(e => e.start() >= viewportEnd); // completely after the viewport
if (nextEvent) {
scheduler.scrollTo(nextEvent.start());
} else {
DayPilot.Modal.alert("No next event found");
}
});
// load initial data
this.loadData();
}
};
app.init(); DayPilot
DayPilot